For IBM i systems not connected to the internet, you can install the IBM and Seiden PHP+ repositories through alternate means.
This article explains two different ways to install open source on your IBM i without a direct internet connection:
- Use an HTTP proxy (for IBM i systems with restricted access, but PCs have access to the outside)
- “Clone” an offline copy of IBM and PHP+ repositories using IBM i Access Client Solutions (ACS). (for sharing with completely airgapped systems)
You’ll need the latest version of ACS as a prerequisite; we recommend at least 1.1.8.5. Older versions do not support repository cloning properly.
HTTP proxy
This method uses ACS to create a proxy on your PC through which your IBM i can connect to the internet.
Starting ACS in proxy mode
From a command prompt on your PC, run java -jar acsbundle.jar /PLUGIN=httproxyui, adjusting the path for the location of “acsbundle.jar”.
Example commands:
# If ACS is in your current directory: java -jar acsbundle.jar /PLUGIN=httpproxyui # Default installation location on Mac: java -jar /usr/local/ibmiaccess/acsbundle.jar /PLUGIN=httpproxyui # Default installation location on Linux: java -jar /opt/ibm/iAccessClientSolutions/acsbundle.jar /PLUGIN=httpproxyui
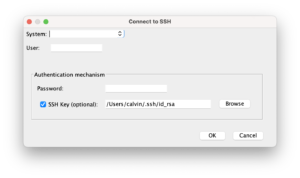
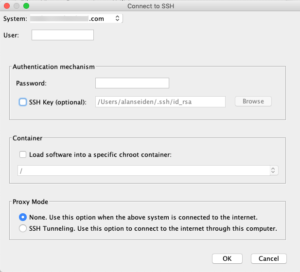
The following dialog will appear. Select your system and enter the credentials needed to log onto SSH. Make sure the SSH daemon is running.
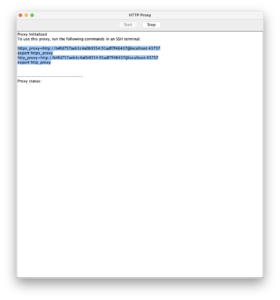
This command launches an HTTP Proxy program that connects to the internet. ACS will then connect using the proxy.
To aid in installing open source, the HTTP Proxy window also provides commands that allow an SSH terminal to use the proxy. When you copy and paste these commands into an SSH terminal, programs in that session will use the HTTP proxy. For example, you can run yum commands on an IBM i system that couldn’t connect to the repository otherwise, and it’ll proxy through your own computer to reach that repository.
To stop the proxy, simply click stop and close the window. You may need to unset the environment variables that were set, such as http_proxy, or simply restart the session.
I get an error about it being it being restricted
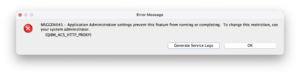
If you get an error as shown below when trying to establish the proxy, make sure your user is authorized to create proxies.
IBM i versions 7.4 and below require a special Program Temporary Fix (PTF) to enable the QIBM_ACS_HTTP_PROXY function. To check whether the PTF is installed, run the appropriate DSPPTF command:
- IBM i 7.2:
DSPPTF LICPGM(5770SS1) SELECT(SI73599) - IBM i 7.3:
DSPPTF LICPGM(5770SS1) SELECT(SI73596) - IBM i 7.4:
DSPPTF LICPGM(5770SS1) SELECT(SI73595) - IBM i 7.5 and up: No PTF needed
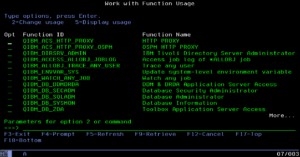
Next, go into WRKFCNUSG on a 5250 screen and change the function QIBM_ACS_HTTP_PROXY so that your user is allowed:
Mirroring the repository
Mirroring the repository will save a copy of the entire repository to your IBM i. This is useful if you intend to install the packages on other systems with restrictive connections, because you can simply copy the directory or host a web server with it.
Connecting to your IBM i
Note that the package management in ACS will require you to run SSH on your IBM i. See the page on how to use SSH. From the main window of ACS, select Open Source Package Management from the main window, or the Tools menu, depending on your version of ACS.
A window will pop up for authentication information for connecting to your IBM i over SSH. Either a password or SSH key (in OpenSSH format; PuTTY format keys must be converted with PuTTYgen. See the page on SSH for how to convert.) can be used; if you aren’t using an SSH key, uncheck the SSH Key box. It will also ask if you’re using a chroot; if you don’t know, you aren’t and can ignore it. If your IBM i isn’t connected to the internet, enable SSH Tunneling. This will let the IBM i connect through your computer to access repositories.
If this is your first time connecting to this IBM i system, the system will prompt to confirm the fingerprint string. The SSH guide explains in detail, but essentially if the fingerprint changes after this initial confirmation, it will warn you.
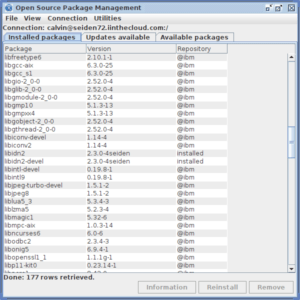
The main window will show the installed packages.
Cloning the repository
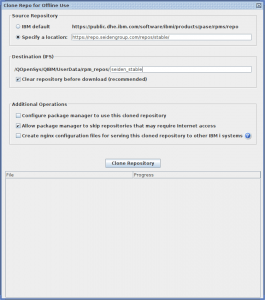
From the ACS main window, select “Utilities” -> “Clone Repo for Offline Use”. Another window will appear with various settings. The most important option here is selecting a custom repository URL.
Click “specify a location,” then specify the URL of the repository you wish to clone (refer to installation instructions for repository URLs, but they all begin with “https://repo.seidengroup.com/repos…” – remove any file such as “repo_name.repo”, since ACS only works with the directory). Finally, specify the directory in which to clone the repo.
Note: the cloning process does not automatically scan dependencies for additional needed repositories. For example, you will probably need to install the IBM repositories no matter what.
Other options:
- Clear repository before download: Remove the contents of the directory you’re cloning to. This saves on disk space by deleting stale packages.
- Configure package manager to use this cloned repository: The clone of this repository will be used by Yum.
- Allow package manager to skip repositories that may require internet access: Leave unchecked unless advised to check it.
- Create nginx configuration files for serving this cloned repository to other IBM i systems: Sets up a web server configuration file for the nginx web server, to serve this directory to other systems. Consult the IBM documentation on cloning for how to use this.
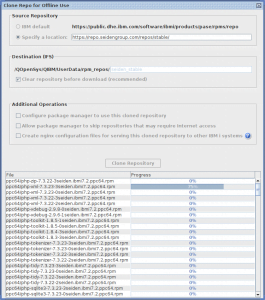
When you hit clone, the bottom part of the window will begin to show the cloning progress.
After you clone a repository, verify that it succeeded by reviewing the repository files in the directory /QOpenSys/etc/yum/repos.d. All locally mirrored repositories should point to IFS locations instead of URLs.